- Pass out the large sheet of poster paper.
- Instruct to fold in half and number like a book/card 1-4.
Agroecosystem Diagram
Graphics designed by: Heather Griffith, UF/IFAS CommunicationsAgroecosystem - the vision of agriculture as an ecological system; environmental and ecological features interact in a dynamic and complex ways [full-sized image]
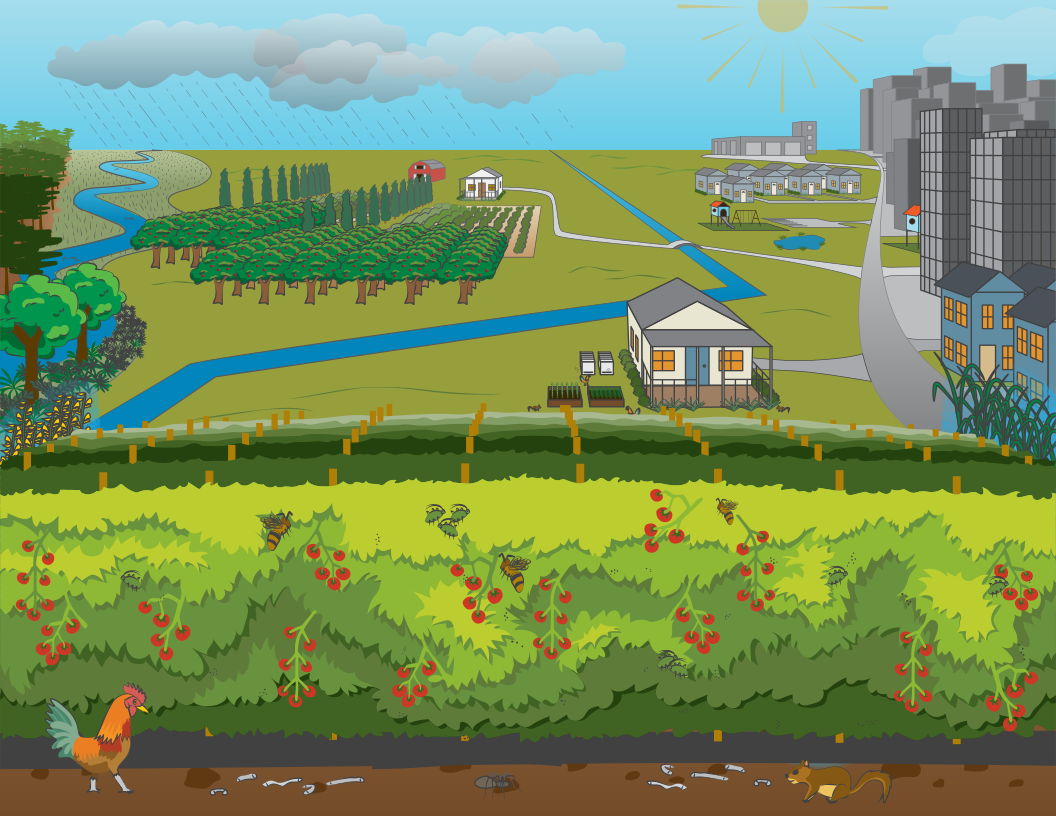
Crop plant - the focus of productivity for the agroecosystem; also might be livestock [full-sized image]

Crop population - grouping of crop plants in monoculture [full-sized image]

Environment - the non-living surroundings that impact crop plant growth; such as water, temperature, light, and soil [full-sized image]

Plant community - the mixture of plants in and surrounding the crop field; some are cooperators and some are competitors [full-sized image]

Invertebrate community - the group of microbes and insects in and surrounding the crop field; some are beneficial and some are harmful [full-sized image]

Vertebrate community - the group of animals in and surrounding the crop field; some are beneficial and some are harmful [full-sized image]

Surrounding land - the land around a farm provides resources and disturbance through the connectivity and interaction with the farm [full-sized image]
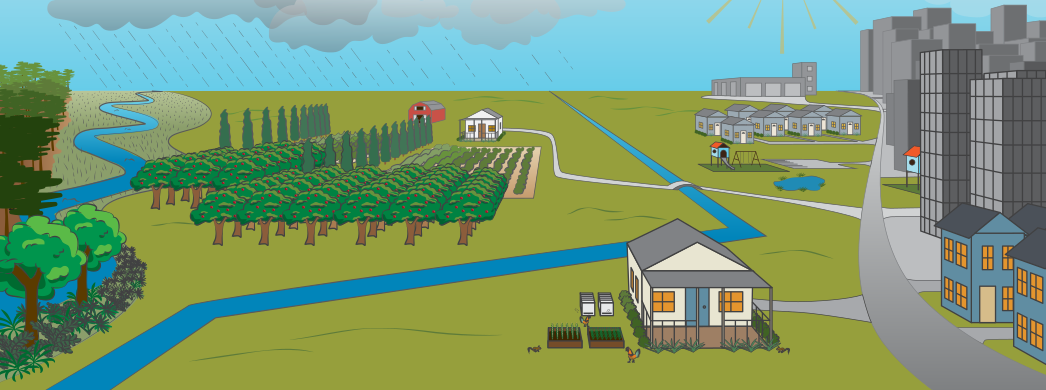
Agroecosystem interactions - organisms that have a positive (in blue) and negative (in red) effect on the crop [full-sized image]

Do Know your Agroecosystem, Step 1
Agroecosystem Awareness
- A way to see the world that you can’t unsee
- All the players in the system and their interactions over space and time
- Practice on our tour, for now…
Do Know your Agroecosystem, Step 2
Agroecosystem Scale and Dynamics
- Organism -> Ecosystem -> Food System
- Space and Time
Do Know your Agroecosystem, Step 3
